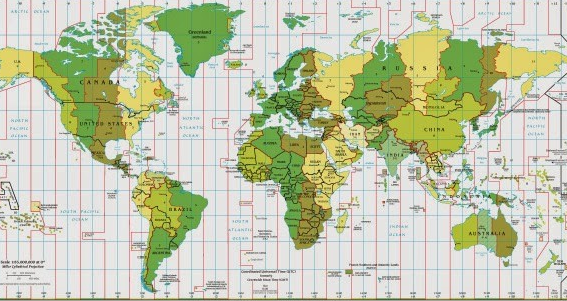
TIME ZONES OF THE WORLD MAP
(Message by Tanny Keng)
a) A time zone is any of the twenty-four divisions of the Earth's surface used to determine a uniform local standard for legal, commercial and social purposes. Each of the zones is about 15° of longitude in width (with local variations) and tends to follow the boundaries of countries and their subdivisions.
b) The 1884 International Meridian Conference, which met in Washington, D.C. at the behest of the President of the United States, established the imaginary prime meridian as the starting reference line for time zones. The meridian (longitude of 0°) runs through the city of Greenwich, England, which is the site of the Royal Greenwich Observatory founded in 1675.
c) What is known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is named after the city and observatory in England. Central European Time, or CET, has also been adopted by Western European countries. It is one hour ahead of GMT.
d) Radio signals have been synchronized to UTC for more than forty years. UTC is based on an atomic clock. Standard time, in most countries, is defined based on UTC (some, like Britain, also use GMT). Also called Zulu time, UTC is used around the globe by astronomers.
i) China contains only one time zone within the country. It additionally has the world's widest spanning zone in terms of land. Before 1949 the country was split into five zones.
ii) There are twenty-two places in the world where three or more time zones meet. One example of this is where the borders of Finland, Norway and Russia meet.
1. Time Zones
a) A time zone is any of the twenty-four divisions of the Earth's surface used to determine a uniform local standard for legal, commercial and social purposes. Each of the zones is about 15° of longitude in width (with local variations) and tends to follow the boundaries of countries and their subdivisions.
b) The 1884 International Meridian Conference, which met in Washington, D.C. at the behest of the President of the United States, established the imaginary prime meridian as the starting reference line for time zones. The meridian (longitude of 0°) runs through the city of Greenwich, England, which is the site of the Royal Greenwich Observatory founded in 1675.
c) What is known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is named after the city and observatory in England. Central European Time, or CET, has also been adopted by Western European countries. It is one hour ahead of GMT.
d) Radio signals have been synchronized to UTC for more than forty years. UTC is based on an atomic clock. Standard time, in most countries, is defined based on UTC (some, like Britain, also use GMT). Also called Zulu time, UTC is used around the globe by astronomers.
2. A separation of dates
a) The International Date Line was created at the International Meridian Conference of 1884 and runs approximately parallel to the 180th meridian. It is an imaginary line man has drawn on the earth to determine when an official calendar day starts. West of the line the day is one day earlier than east of the line.
a) The International Date Line was created at the International Meridian Conference of 1884 and runs approximately parallel to the 180th meridian. It is an imaginary line man has drawn on the earth to determine when an official calendar day starts. West of the line the day is one day earlier than east of the line.
3. Saving Daylight
a) Many countries have, for at least part of a year, adopted daylight saving (DST). DST usually means putting all clocks ahead one hour near the beginning of spring and putting them back an hour in the Fall. The 'saving' of daylight was first proposed in 1907. It was not widely used until World War I when it was viewed as a means of preserving coal reserves. Despite its controversies many countries use DST.
a) Many countries have, for at least part of a year, adopted daylight saving (DST). DST usually means putting all clocks ahead one hour near the beginning of spring and putting them back an hour in the Fall. The 'saving' of daylight was first proposed in 1907. It was not widely used until World War I when it was viewed as a means of preserving coal reserves. Despite its controversies many countries use DST.
4. Fast Facts
a) America and its territories have ten zones.
a) America and its territories have ten zones.
i) China contains only one time zone within the country. It additionally has the world's widest spanning zone in terms of land. Before 1949 the country was split into five zones.
ii) There are twenty-two places in the world where three or more time zones meet. One example of this is where the borders of Finland, Norway and Russia meet.
iii) Due to seasonal differences in sunlight being small, many equatorial countries do not observe DST.
The End ...

Comments
Post a Comment